Project Description
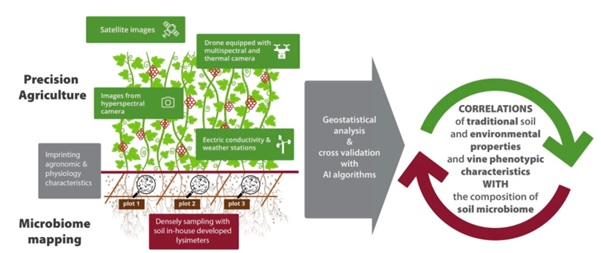
DiVine is going to contribute to the optimisation of vineyard production through the adoption of a novel approach based on the establishment of correlations between crop characteristics, available from PA- enabled observations and agronomic measurements (phenotype), and soil microbiome characteristics, obtained from the application of Biotechnology-related processes, as well as the identification of how crop- related macro and microscopic parameters may combinedly affect the yield and quality of vine production. It will pave the way to establish cost and time efficient macroscopic and observation criteria and methodology to link phenotype to the rather costly and elusive genotype of microbiome in vineyards. Food safety, pathogen prevention and climate change are just a few of the many sectors that would benefit hugely from an efficient correlation of phenotype to genotype with huge impact on public health, food quality and agricultural economy.
Objectives:
- Contribute to the realisation of synergies between the research fields of Precision Agriculture and Biotechnology targeting at beyond the state-of-the-art research for the sake of sustainable Agriculture.
- Establish new agricultural research paths by trying to quantify and qualify the impact of the soil microbiome through its influence on agronomic traits measured by PA sensing devices.
- The repositioning of Agriculture from traditional hard labor to a knowledge-based and high-tech endeavour to change the profession of the farmer drastically and will, in turn, draw people from other fields of expertise into the agri-food sector.
Potential Impact:
- Scientific impact
- Establish synergies between PA-enabled practices and Biotechnology.
- Develop and provide a novel, holistic approach to the treatment of vineyards and production optimisation.
- Impact on agriculture
- Showcase the influence of microbiome in agronomic practices and establish new research and commercial opportunities.
- Help farmers understand the needs of their crops.
- Socio-economic impact
- New market and business opportunities.
- Inclusion of ICT technologies and microbiome control techniques in the field.